
Click the “Select File” button and select the SPMetadata.xml file you got from Splunk.Click the Create button at the top right of the table.In the Keycloak admin console, click on Clients in the menu on the left.Click the “Download File” button to get the metadata configuration to import into Keycloak.Select SAML Authentication and click “Configure Splunk to use SAML”.In Splunk, navigate to the Settings menu (in the top right) → Users and Authentication → Access Controls.
SPLUNK AUTHENTICATION CONF LICENSE
SPLUNK AUTHENTICATION CONF PASSWORD
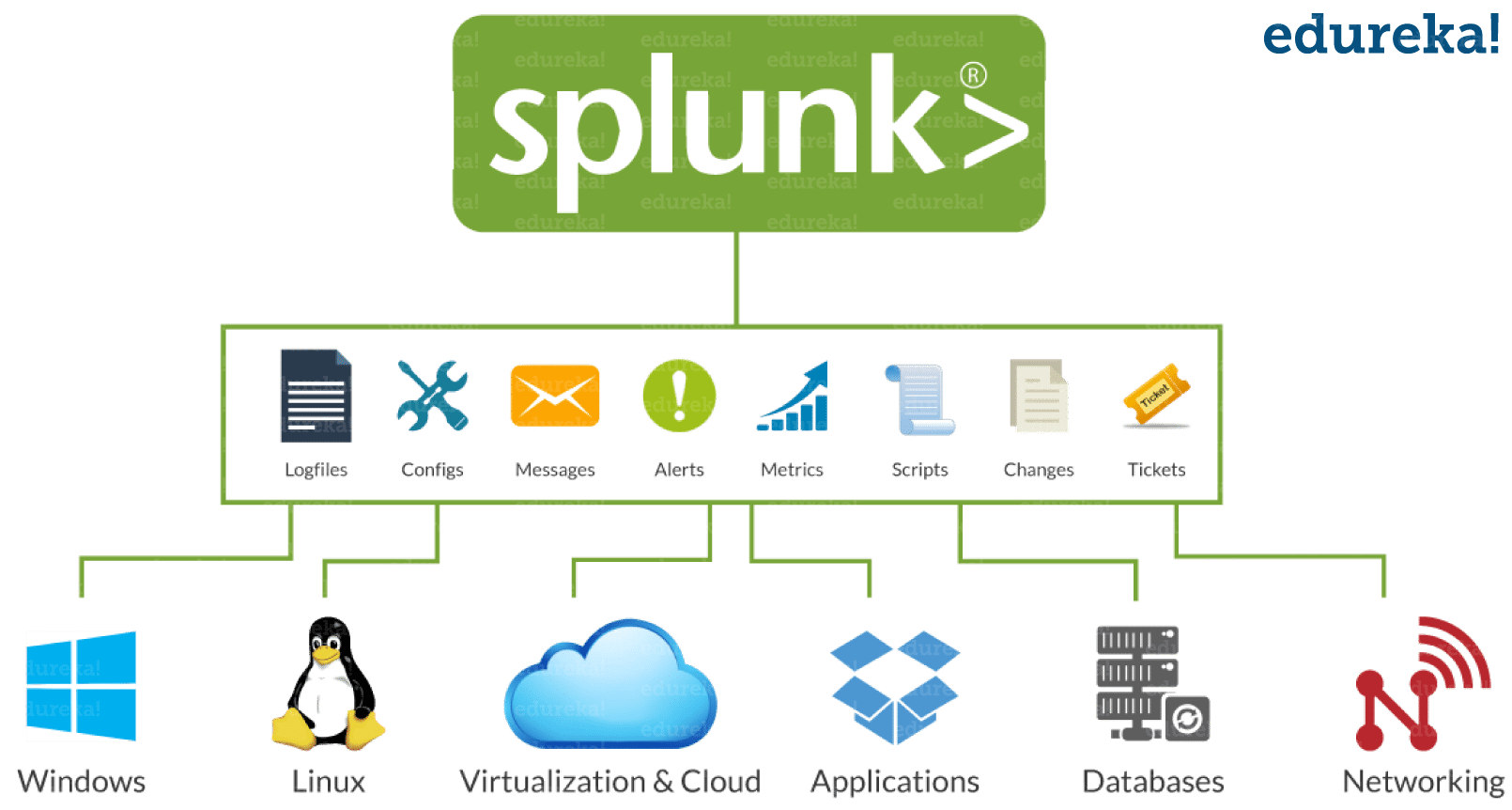
In the ‘Credentials’ tab for your user, set a password.Navigate to Manage → Users via the menu on the left.Add two new roles: reportingadmin and reportingviewer.Navigate to Configure → Roles via the menu on the left.Log into the Keycloak web interface at localhost:8080 using the username admin and password Pa55w0rd.You can comment the service out or delete it from the docker-compose.yml to save some build time Clone the repo and start up the Docker environment with: docker-compose up -d.Start a Keycloak server instance, we used my keycloak-react-app project Splunk will prevent the user from deleting an LDAP or SAML account.Here are the steps we used to successfully configure Keycloak as the IdP for Splunk via SAML If the nf file does not exist, copy the file from /etc/opt/splunk/system/default to the /etc/opt/splunk/system/local directory.Ĭonfigure minimum settings similar to the example below for using LDAP or SAML.Įdit the following file in the /etc/openldap folder:Ĭonfigure the following lines for your certificate.Īfter configuring LDAP or SAML, open the Splunk Web console.Ĭreate appropriate LDAP and SAML users and groups for the environment.ĭelete any user account with Authentication system set to Splunk, with the exception of one emergency account of last resort. This configuration is performed on the machine used as a search head or a deployment server, which may be a separate machine in a distributed environment. If any user accounts have Authentication system set to Splunk, with the exception of one emergency account of last resort, this is a finding. Verify that no user accounts exist with Authentication system set to Splunk except an account of last resort. Select Settings > Access Controls > Users. If any are missing or do not match the settings below, this is a finding. If the file does not exist, this is a finding.Ĭheck for the following lines. If any minimum settings are not configured, this is a finding.Ĭheck the following file in the /etc/openldap folder: In the nf file, verify minimum settings similar to the example below. If the nf file does not exist, this is a finding. Navigate to the /etc/opt/splunk/system/local/ directory. This check is performed on the machine used as a search head or a deployment server, which may be a separate machine in a distributed environment. Splunk Enterprise 8.x for Linux Security Technical Implementation Guideĭetails Check Text ( C-55117r808271_chk ) Organizational users must be uniquely identified and authenticated for all accesses. Sharing of accounts prevents accountability and non-repudiation. To assure accountability and prevent unauthenticated access, organizational users must be uniquely identified and authenticated to prevent potential misuse and compromise of the system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
